No further increase in medical aids

A majority in the older population used medical aids in 2008. The proportion using aids increased over the period 2001–2005. Despite the fact that the Dutch population is ageing, the proportion did not increase further since 2005.
Proportion of people wearing glasses stable since 2001
Last year, six in ten people aged four years and older living in private households wore glasses or used other (audio-)visual aids. The proportion has hardly changed since 2001.
Proportion in the Dutch population using mobility or hearing aids

Between 2001 and 2005, the proportion of people using mobility or hearing aids was still growing and subsequently stabilised. Last year, 5 percent used devices to improve their mobility, like walking sticks or walkers; 3 percent used hearing aids or other special devices to amplify sounds.
Partly as a result of the ageing process, the number of persons using aids continued to grow after 2005. In 2008, for example, more than 530 thousand people used mobility aids, as against 520 thousand in 2005 and 380 thousand in 2001.
Mobility aids by age, 2008
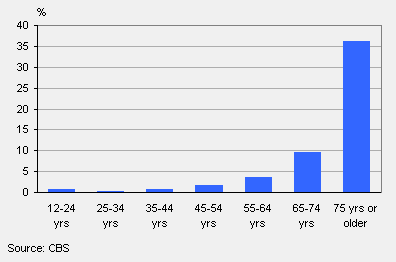
Medical aids predominantly used by older people
Older people were the most frequent users of medical aids. Virtually all over-65s wore glasses or other devices to improve their vision in 2008. Three quarters of the 530 thousand people using mobility aids were 65 years or older.
Twice as many older women than men used devices to improve their mobility in 2008. One quarter of women aged 65 and older used walking sticks, crutches or walkers; 7 percent used wheelchairs or mobility scooters.
Older men, on the other hand, more often wore hearing aids or other devices to amplify sounds. Nearly 20 percent of men wore hearing aids, as opposed to 16 percent of older women.
Proportion in the Dutch population using mobility aids by income and level of education

Lower income brackets use more medical aids
Apart from age, education level and income also appeared to be important factors in the category of people using mobility aids. Lower educated people and people living on lower incomes, more often used mobility aids. People in the lowest income bracket used mobility aids three times as often as those in the highest income bracket.
Marleen Wingen