Use of green electricity growing

In 2004 nearly 38 percent of Dutch households used green electricity, an increase by 6 percentage points on 2003.
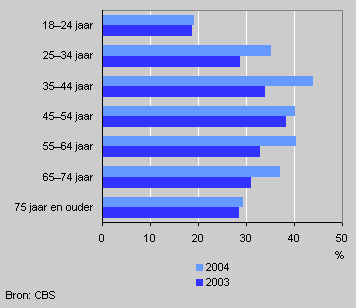
The increase is largely due to households whose breadwinner is aged between 35 and 44. Among these households the use of green electricity rose from 34 to 44 percent. With 19 percent, the use of renewable electricity was lowest among households whose breadwinner was in the age category 18–24.
Households using green electricity by age of the breadwinner
Higher educated people more often use green electricity
Over 45 percent of households whose breadwinner is highly educated used green electricity in 2004. The category households whose breadwinner is lower educated accounts for only 33 percent. Use of green electricity was also significantly lower among singles (34 percent) than among families with children (more than 43 percent).
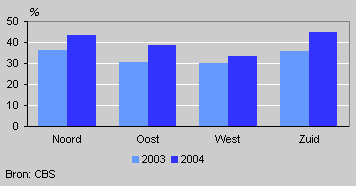
Use of green electricity by part of the country
Most common in rural communities
The use of green electricity is most common in rural communities, i.e. 43 percent in 2004, whereas in areas with a very high urbanisation rate close to 35 percent of households signed up with green electricity providers. In the provinces of North Brabant and Limburg the use of green electricity was nearly 45 percent. In the four western provinces it was only 33 percent. Typically, green electricity is more common among house-owners (42 percent) than among tenants (33 percent). This is probably due to the fact that most contracts of young tenants do not include the possibility to opt for green electricity.
Lowest income brackets have lowest use rate
With 34 percent, the use of green electricity was lowest among households earning a net annual income below 13 thousand euro. Households whose net annual income ranged from 25 to 36 thousand euro recorded the highest use (44 percent). Nearly 40 percent of households whose net annual income exceeded 36 thousand euro, used green electricity. It should, however, be borne in mind that net annual household incomes largely depend on the age and the level of education of the breadwinner.
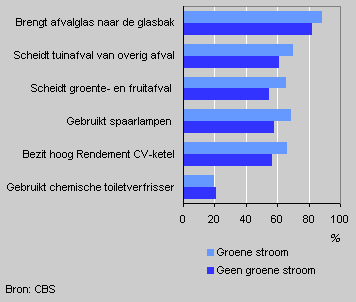
Environmental awareness of households by electricity use
More environmental awareness among users of green electricity
Households using electricity from renewable sources are better aware of the environment. Over 66 percent of these households separated vegetable, fruit and garden waste from other waste in 2004. Thus their environmental awareness exceeded that of other households by more than 9 percentage points.
The use of energy-saving bulbs was also more common among users of green electricity. On the other hand, the use of artificial toilet fresheners was evenly spread among users and non-users of green electricity.
Ger Sleijpen