Age, sex and education level affect hourly wages

The hourly wage rate of employees averaged more than 17 euro by the end of 2002. On average women earned one fifth less than men. Hourly wages of employees ranged from almost 13 euro for employees with only primary education to almost 28 euro for university-educated employees.
Over one-third of jobs at mbo level
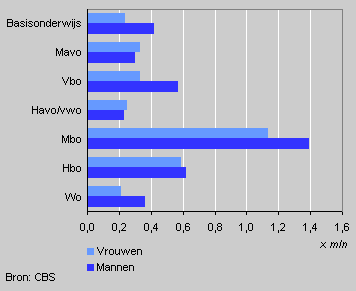
By the end of 2002 there were almost 7 million jobs of employees in the Netherlands and 56 percent of these jobs were held by men. The most common level of education is mbo (senior vocational education), with 36 percent, followed by hbo (vocational college) and vbo (pre-vocational education) with 17 and 13 percent respectively. More than 60 percent of jobs at the level of primary education, vbo and wo (university education) are held by men. Jobs at senior general secondary education and pre-university level (havo/vwo) and junior general secondary education level (mavo) are mostly held by women.
Jobs by education level and sex, end of 2002
Average hourly wages women one fifth lower
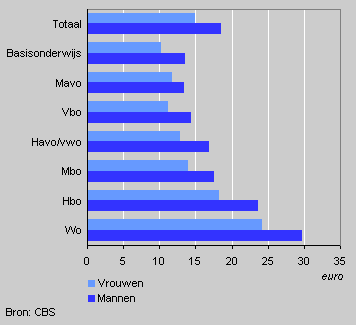
The average hourly wage in 2002 amounted to 17.24 euro. The better employees are educated, the more they earn. The hourly wage of university-educated employees was 2.2 times as high as the hourly wage of employees with only primary education. Hourly wages of women were 19 percent below men’s hourly wages. At all levels of education women earn less than men. The largest gap is found among primary school-educated employees (25 percent), the smallest difference is found among mavo-educated employees (13 percent).
Hourly wages by education level and sex, end of 2002
Hourly wage strongly related with age
Apart from education level and sex, hourly wages are also affected by age. They increase with advancing age. Employees in the age category 55-64 earn 2.3 times as much as employees aged 15-24.
Differences in hourly wages between men and women, end of 2002
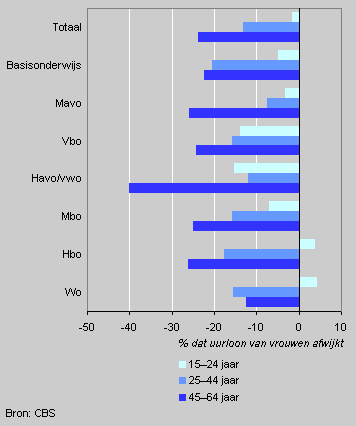
Wage differences by sex and age
The difference in hourly wage rate is relatively small for young men and women. In the age category 25-44 women’s wages at all levels of education (except mavo) were between 10 and 20 percent below men’s wages. The largest discrepancy is found in the age group 45-64. Women’s wages were on average 20 percent below men’s wages for almost the entire age group. For employees at senior general secondary education level (havo/vwo) the difference was no less than 40 percent.
Jo van Cruchten and José Gouweleeuw